目录
2024年3月27日星期三
今天学到了动态SQL,以下全是我个人总结的,如果有问题可以联系我修改👀
第三章 动态SQL
学习目标
- 掌握MyBatis中动态SQL元素的使用
- 掌握MyBatis中条件查询操作
- 掌握MyBatis的更新操作
- 掌握MyBatis的复杂查询操作
在实际项目的开发中,开发人员在使用JDBC或其他持久层框架进行开发时,经常需要根据不同条件拼接SQL语句,拼接SQL语句时还要确保不能遗漏必要的空格、标点符号等,这种编程方式给开发人员带来了极大的不便,而MyBatis提供的SQL语句动态组装功能,恰能很好地解决这一问题。
3.1 动态SQL中的元素
动态SQL是Mybatis的强大特性之一,MyBatis采用了功能强大的基于对象导航图语言(Object Graph Navigation Language,OGNL)
| 元素 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| <if> | 判断语句,用于单条件判断 |
| <choose> (<when>、<otherwise>) | 相当于Java中的switch...case...default语句,用于多条件判断 |
| <where> | 简化SQL语句中where的条件判断 |
| <trim> | 可以灵活低去除多余的关键字 |
| <set> | 用于SQL语句的动态更新 |
| <foreach> | 循环语句,常用于in语句等列举条件中 |
以上是MyBatis动态SQL中常用的一些元素,下面将对这些动态SQL元素的使用进行详细讲解。
3.2 条件查询操作
3.2.1 <if>元素
<if>元素是最常用的判断元素,类似于Java中的if语句,主要实现某些简单的条件判断。
运用场景:当某个用户填写信息时,可以通过姓名或者年龄来查找用户,也可以不填写年龄直接通过姓名来查找用户,可以什么都不填写查询出所有用户,此时的姓名和年龄就是非必需条件,
以上情况就可以使用<if>元素来实现。
1. 数据库准备
在名为mybatis的数据库中,创建一个t_customer数据表,并插入几条测试数据,具体代码如下:
SQLuse mybatis;
create table t_customer (
id int(32) primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(50),
jobs varchar(50),
phone varchar(16)
);
insert into t_customer values ('1','joy','teacher','13733333333'),('2','jack','teacher','13522222222'),('3','tom','worker','15111111111');
2. POJO类准备
在org.example.pojo包下创建持久化类Customer,在类中声明id、username、jobs和phone属性,以及对应的getter/setter方法。
Javapublic class Customer {
private int id; //客户id
private String username; //客户姓名
private String jobs; //职业
private String phone; //电话
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getJobs() {
return jobs;
}
public void setJobs(String jobs) {
this.jobs = jobs;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
}
3. 创建映射文件
在项目src/main/resources/mapper包下创建映射文件CustomerMapper.xml ,在映射文件中,根据客户姓名和年龄组合成的条件查询客户信息,使用<if>元素编写该组合条件的动态SQL。
xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.example.pojo.Customer">
<!--<if>元素使用-->
<select id="findCustomerByNameAndJobs" parameterType="org.example.pojo.Customer" resultType="org.example.pojo.Customer">
select * from t_customer where 1=1
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs != ''">
and jobs like concat('%',#{jobs}'%')
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
使用<if>元素的test属性分别对username和jobs进行非空判断,
注意
注意 :where 1=1 是为了防止 if内执行的语句无法使用 ,凭空多出一个 and username like concat('%',#{username},'%') 语句 SQL就无法执行,为什么要加 where 1=1呢 如果不加的话后面if里面的语句就执行不到就会因为没有 where 关键字导致错误,为什么 要加上 1=1 呢因为这种情况是因为用户什么都没输入的情况,就会去查询所有记录。
4. 修改核心配置文件
在配置文件mybatis-config.xml中,引入CustomerMapper.xml映射文件到<mappers>元素中
xml<mapper resource="mapper/CustomerMapper.xml"/>
5.创建获取SQlSession对象
Java String resources = "mybatis-config.xml";
//创建流
Reader reader = null;
try {
//读取mybatis-config.xml文件到reader对象中
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//初始化Mybatis数据库,创建SqlSessionFactory类的实例
SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
//创建SqlSession实例
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
6. 修改测试类
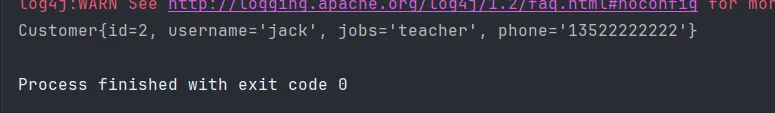
添加测试方法 findCustomerByNameAndJobs()
Java @Test
public void findCustomerByNameAndJobs(){
String resources = "mybatis-config.xml";
//创建流
Reader reader = null;
try {
//读取mybatis-config.xml文件到reader对象中
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//初始化Mybatis数据库,创建SqlSessionFactory类的实例
SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
//创建SqlSession实例
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
//获取Customer对象
Customer customer = new Customer();
//设置属性值
customer.setUsername("jack");
customer.setJobs("teacher");
List<Customer> customers = session.selectList("org.example.pojo.Customer.findCustomerByNameAndJobs", customer);
for (Customer customer1 : customers) {
System.out.println(customer1.toString());
}
session.close();
}
运行成功截图
3.2.2 <choose>、<when>、<otherwise>元素
在使用<if>元素时,只要test属性中的表达式为true,就会执行元素中的条件语句,但是在实际应用中,有时只需要从多个选项中选择一个去执行。
使用场景:
当客户名称不为空,则只根据客户名称进行客户筛选。
当客户名称为空,而客户职业不为空,则只根据客户职业进行客户筛选。
当客户名称和客户职业都为空,则要求查询出所有电话不为空的客户信息。
这种场景下使用<if>元素进行处理是非常不合适的,MyBatis提供了<choose>、<when>、<otherwise>元素进行处理。接下来将演示如何使用<choose>、<when>、<otherwise>元素。
(1)在映射文件CustomerMapper.xml中,添加使用<choose>、<when>、<otherwise>元素执行上述情况的动态SQL
xml <select id="findCustomerByNameOrJobs" parameterType="org.example.pojo.Customer" resultType="org.example.pojo.Customer">
select * from t_customer where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="username != null and username !=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username}'%')
</when>
<when test="jobs != null and jobs != ''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</when>
<otherwise>
and phone is not null
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
(2) 在测试类中,编写测试方法findCustomerByNameOrJobsTest()
Java @Test
public void findCustomerByNameOrJobsTest(){
String resources = "mybatis-config.xml";
//创建流
Reader reader = null;
try {
//读取mybatis-config.xml文件到reader对象中
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//初始化Mybatis数据库,创建SqlSessionFactory类的实例
SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
//创建SqlSession实例
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
//创建customer对象
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("tom");
customer.setJobs("teacher");
List<Customer> customers = session.selectList("org.example.pojo.Customer.findCustomerByNameOrJobs",customer);
for (Customer customer1 : customers) {
System.out.println(customer1.toString());
}
session.close();
}
运行成功截图
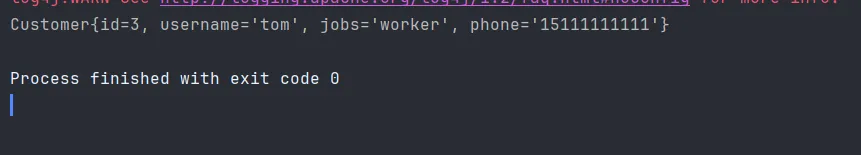
由上图可见,只要条件满足条件的when,就会执行里面的sql语句,尽管tom的职业不是teacher,也一样能查询出来,更改代码
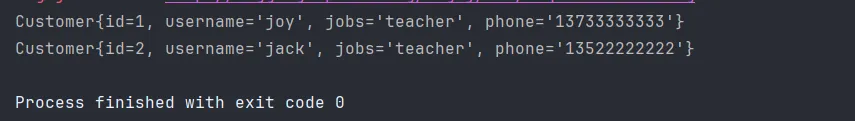
Java //customer.setUsername("tom");
将以上代码注释后就会满足第二个when的条件就会查询出所有职业为 teacher 的客户
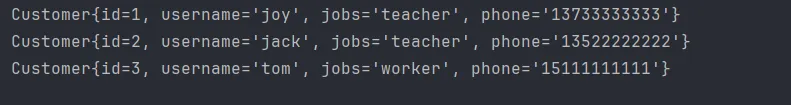
将以下代码也注释后就会执行<otherwise>中的条件,就会查询出所有用户的phone
Java customer.setJobs("teacher");
运行截图
**未完待续...... **
本文作者:苏皓明
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!